Have you ever seen a piece of rough metal whizzing around on a lathe and then be turned out to a bright, much-precise-made part in a few minutes? That is the instance that evokes curiosity and admiration for the machine in action. Since the distant past, lathes have driven forward the backbone of forward-thinking, and in today's times, they still define industries. In a small repair shop and a great aerospace plant, you will find a lathe turning slowly and carving. All lathes, however, do not behave or appear alike.
Each type will fit a distinct need, and the selection of the appropriate one may result in an increase in output, minimization of waste, and the generation of ideas for new products. We are going to look at each of the significant categories of lathe machines, get into their components, compare each, and learn the tips that you can use when you want to select the ideal machine in your workshop. Grab your seat, at the end you will be an expert in lathes.
Lathe Basics: How One Simple Motion Delivers Countless Shapes
A lathe grips the work between two points or into a jaws-like device called a chuck and rotates the object about a stationary spindle while using a sharp object to excavate material. This basic turning motion results in cylinders, tapers, threads, and very intricate curves. Key parts include:
● Bed: Rigid base that supports every other element.
● Headstock: Houses the main spindle, speed controls, and drive motor.
● Tailstock: Supports the free end of long work or holds tools like drills.
● Carriage: Slides along the bed to move the cutting tool.
● Tool post: Clamps and positions the cutting tool.
● Lead screw & feed rod: Coordinate tool motion for threading or smooth cuts.
Add modern controls, quick-change gearboxes, and digital displays, and the lathe becomes a powerhouse of both speed and accuracy.
Why Classifying Lathes Matters?
Every workshop tackles different jobs: small parts in high volume, giant shafts in ones and twos, or prototypes that change by the hour. A lathe built for one task may slow you down on another.
When you know the main categories, you can match machine to mission, cut setup time, and reach the finish line faster. In the next sections, we will walk through each major class, noting size, speed, tooling, and best uses.
Quick Comparison of Common Lathe Types
Before you decide which lathe to buy, it helps to see the choices at a glance. The short table below lists the most common types, what they do best, the kind of parts they handle, and one key drawback to remember. Use it as a quick guide, then look at the full article when you need more detail.
|
Lathe type |
What it does best |
Typical part size |
One key limit |
|
Engine (center) |
Good all-rounder for repair jobs and one-off parts |
Small to large shafts and sleeves |
Not the fastest for high-volume runs |
|
Bench |
Fine, small work in tight spaces |
Tiny pins, hobby parts |
Limited power and swing |
|
Speed (wood/metal) |
Very quick turning and polishing |
Light pieces up to hand size |
No power feeds or threading gears |
|
Toolroom |
High-accuracy wo,rk such as gauges and molds |
Small to medium parts |
Higher cost than a standard engine lathe |
|
Turret/Capstan |
Repeats of short parts with many tools ready to go |
Nuts, bushings, fittings |
Setup takes time; less flexible than CNC |
|
CNC 2-axis |
Precise, repeatable parts with easy program changes |
Small to medium work |
Needs skilled programming and a higher budget |
|
Swiss-type |
Long, slender pieces that must stay rigid |
Medical screws, watch stems |
Suited only to small diameters |
|
Vertical (VTL) |
Large, heavy discs that are hard to lift sideways |
Pump housings, turbine cases |
Big footprint and cost |
CNC Lathe
Computer numerical control (CNC) transformed turning by linking motors on every axis to a programmable brain. CNC lathe reads a G-code file and executes each move with repeatable accuracy.
Core Elements
● Servo-driven X and Z slides.
● Spindle with feedback sensor and wide speed range.
● Turret or gang tool plate for quick tool swaps.
● Enclosure with coolant system and chip conveyor.
Advantages
● Switch from one part to another in minutes by loading a new program.
● Keep tight tolerances across long runs.
● Handle complex profiles, threads, and grooves without special gears or cams.
● Collect data for quality control and predictive maintenance.
Sub-Types
1. 2-Axis CNC Lathe: Basic turning and facing.
2. C-Axis or Live-Tool Lathe: Adds milling, drilling, and tapping in one setup.
3. Multi-Turret Lathe: Two or three turrets cut at once for shorter cycle times.
4. Mill-Turn Center (Turn-Mill): Full five-axis machining with B-axis head.
From smartphone housings to rocket parts, CNC lathes keep production lines agile and cost-effective.
Engine Lathe (Center Lathe)
The engine lathe sits at the center of most training rooms and job shops. Its name dates back to steam-powered factories, yet today’s models run on quiet electric motors with variable speed drives.
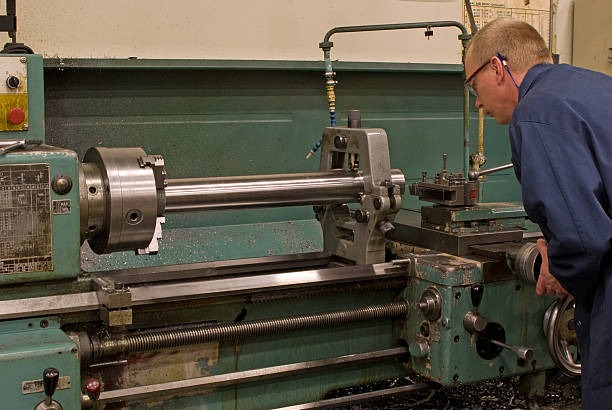

Features
● Swing (diameter capacity) from 150 mm up to 1 m or more.
● Bed lengths between 500 mm and 6 m.
● Quick-change gearbox for many thread pitches.
● Manual handwheels plus powered cross and longitudinal feeds.
● Handles one-off parts, maintenance jobs, and small batches.
● Accepts chucks, centers, faceplates, and steady rests for a wide variety.
● Easy to learn, perfect for teaching basics.
Shaft repairs, bushings, small molds, prototype fittings, or any task that demands flexibility. If you need a “do-everything” lathe, start here.
Speed Lathe
A speed lathe sacrifices heavy horsepower for very high rotation rates. Jewelers, wood turners, and polishing shops rely on this quick machine.
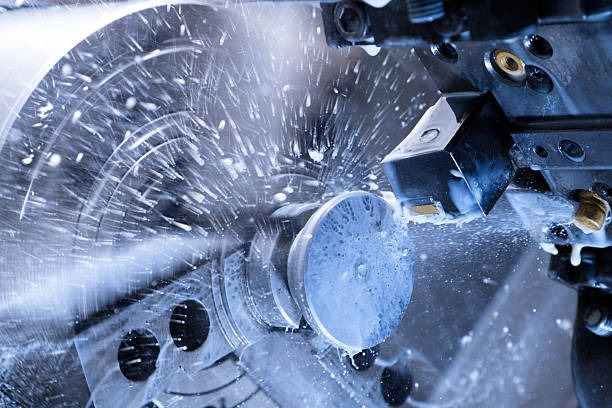

Features
● Light bed and simple drive.
● Two or three belt-selected speeds, often topping 3,000 rpm.
● No power feeds, threading gears, or lead screw.
● Compact footprint, often bench-mounted.
Ideal Tasks
● Turning wood spindles, bowls, or pens.
● Polishing or buffing metal shafts.
● Rapid deburring of small parts.
If your goal is a fast surface finish on light materials, the speed lathe shines.
Bench Lathe
A bench lathe packs full metal-cutting strength into a frame that sits on a sturdy tabletop. Hobbyists, watchmakers, and small labs appreciate its convenience.
Features
● Swing: 75 mm – 200 mm.
● Bed length: 250 mm – 500 mm.
● Variable-speed DC or brushless motor.
● Precise cross slide with micrometer dials.
Reasons to Choose
● Fits cramped spaces without losing accuracy.
● Cuts brass, aluminum, mild steel, and plastics.
● Quick to set up for fine threading, knurling, and facing.
Many prototypes start life on a bench lathe before moving to large production cells.
Toolroom Lathe
When the job calls for tenths of a millimeter or closer, the toolroom lathe answers. It blends a rugged build with silky slides and tight spindle runout.
Features
● Hardened and ground bed ways.
● Extra gear ranges for slow, smooth finishing cuts.
● Built-in collet closer for minimal part runout.
● Often includes digital readouts (DRO) on all axes.
Use Cases
● Cutting master gauges, jigs, and fixtures.
● Producing die punches or mold cores.
● Research labs where repeatable accuracy is vital.
Yes, you pay more for this class, but the savings in scrap and rework soon repay the cost.
Gap-Bed Lathe
Imagine turning a long shaft with a wide pulley near one end. A standard bed gets in the way. The gap-bed lathe solves this by letting you remove a section near the headstock, opening a wider swing for a short length.
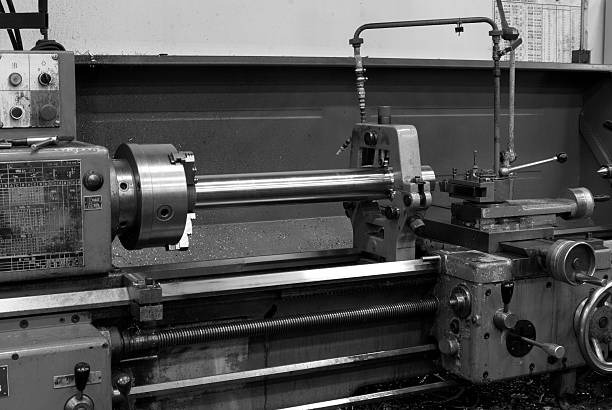

Features
● Removable bed segment increases swing by 50 %–100 %.
● Rest of bed keeps normal height and stiffness.
● Ideal for pump housings, ship propeller shafts, or large flanges.
Machinists slide the segment out only when needed, so daily operations stay rigid and aligned.
Copy (Duplicating) Lathe
A copy lathe traces a master template or an electronic profile and cuts new workpieces to match. Think of banister rails, gun stocks, or custom car parts where every piece must match a shape, but production runs stay moderate.
How It Works
● Hydraulic or electronic sensors follow a stylus along the pattern.
● Signals move the cross slide in real time.
● Tool reproduces curves and tapers with little manual input.
Benefits
● Reduces the manual skill needed for complex contours.
● Speeds up small-batch wood or metal part runs.
● Maintains uniformity across parts that look hand-carved.
Turret Lathe
The turret lathe mounts six or eight tools on a rotating turret. Operators index the turret after each cut, which slashes changeover time and pushes parts out faster.
Features
● Fixed saddle holds heavy turret; bed remains short and stiff.
● A bar feeder often pushes stock through a hollow spindle.
● Multiple cross slides can carry form tools or cut-off blades.
Fittings, bushings, valve stems, and other turned components are needed in thousands. While CNC lathes now dominate large plants, manual turret lathes still thrive in low-to-medium volume shops where setup cost matters.
Capstan Lathe
A capstan lathe shares the turret concept but keeps it on a light, slide-mounted ram. This lets the turret move back quickly for short, repetitive operations on small bars.
Features
● Fast hand lever feeds.
● Limited travel, so suited to parts under 75 mm long.
● Smaller swing than a full turret lathe.
Capstan lathes once filled factories making screws, nuts, and instrument parts. In many regions, they still offer a low-investment path to mass production.
Automatic Lathe
An automatic lathe performs all tool indexing, feeds, and stock advances by cams or servo drives. Operators only load bar stock and collect finished parts.
Features
● Consistent cycle times day and night.
● High output for simple parts like fasteners and hydraulic fittings.
● Minimal skilled labor once set up.
Limitations
● Cams take time to design and grind.
● Less flexible than CNC when part mix changes often.
Still, for one part in a huge volume, the automatic lathe pays for itself quickly.
Special-Purpose Lathes
Each special-purpose lathe proves that turning technology bends to fit even the toughest job.
Wheel Lathe
Designed to re-profile train wheels without removing them from the axle. Huge swing, deep horsepower, and hardened ways let it cut steel rims smooth and true.
Crankshaft Lathe
Extra support, steady rests, offset chucks, and custom tooling shape crank throws with high strength.
Vertical (VTL)
Flips the axis upright so gravity supports large discs like turbine casings or pump bodies. Operators stand at floor level, easing loading.
T-Lathe
Named for its T-shaped bed, this lathe turns long rolls used in paper mills or steel plants. One cross slide works near the headstock, while another rides the long bed.
Multi-Spindle Lathe
Picture six workstations in a circle, each holding its part, tool, and feed system. The drum indexes, and every station cuts at once. After one full rotation, six complete parts drop out.
Features
● Ideal for screws, pins, and bushings under 30 mm diameter.
● Cam-controlled or CNC-controlled versions exist.
● Cycle times as short as a few seconds.
Multinationals still choose multi-spindle lathes when millions of identical parts justify the higher capital cost.
Swiss-Type Lathe
A Swiss lathe guides bar stock through a close, sliding guide bushing. The cutting tool sits very close to the support point, which stops long, thin parts from flexing.
Features
● Handles diameters from 0.3 mm to 32 mm.
● Up to 12 or more axes for cross drilling, milling, and slotting.
● Sub-spindle catches the part, allowing back-working.
Swiss lathes dominate watchmaking, medical screws, and electronic connectors—any field that lives on small, precise, slender forms.
Choosing the Right Lathe
When you shop for a lathe, match the machine to the workload using these factors:
1. Workpiece Size: Measure swing, length, and weight.
2. Volume: High volume favors CNC or automatic styles; one-offs lean on engine or bench lathes.
3. Tolerance Needs: Toolroom or CNC machines reach tighter limits than a speed lathe.
4. Materials: Tough alloys need more horsepower and rigid beds.
5. Floor Space and Power: Check footprint and electrical supply.
6. Skill Level: Manual lathes demand hands-on skill; CNC requires programming know-how.
7. Budget: Add tooling, fixtures, and training to the purchase price.
A clear list of parts and growth plans makes the choice easier and guards against costly oversights.
Safety Practices for Every Lathe
Good habits protect both workers and machines from harm and downtime.
● Wear snug clothing and eye protection.
● Keep chips clear; use a brush, not your bare hands.
● Check tool sharpness and correct height each shift.
● Set guards and covers before you start.
● Never leave the chuck key in place.
● Stand clear of rotating stock ends.
● Use the correct cutting speed to avoid tool breakage.
● Shut off power before measurements or tool changes.
Conclusion
Lathes started as simple foot-powered spindles and grew into today’s smart, connected machining centers. Each type—engine, speed, bench, toolroom, turret, capstan, automatic, CNC, and many more—earns its place by solving a clear set of problems.
With that knowledge of the differences, you can achieve a match between machine and mission, increase productivity, and tap other sources of ideas in restructuring your shop. With the information in this guide, determine the strength of your needs, the right questions, and make confident investments. As long as you make the right choice, your workshop will never get tired of turning a profit with a good lathe.