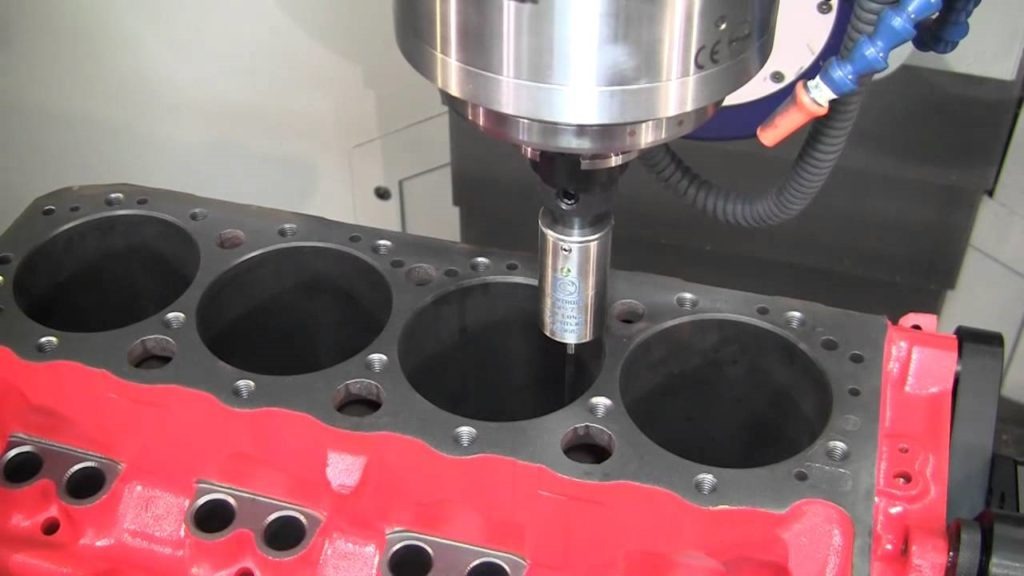
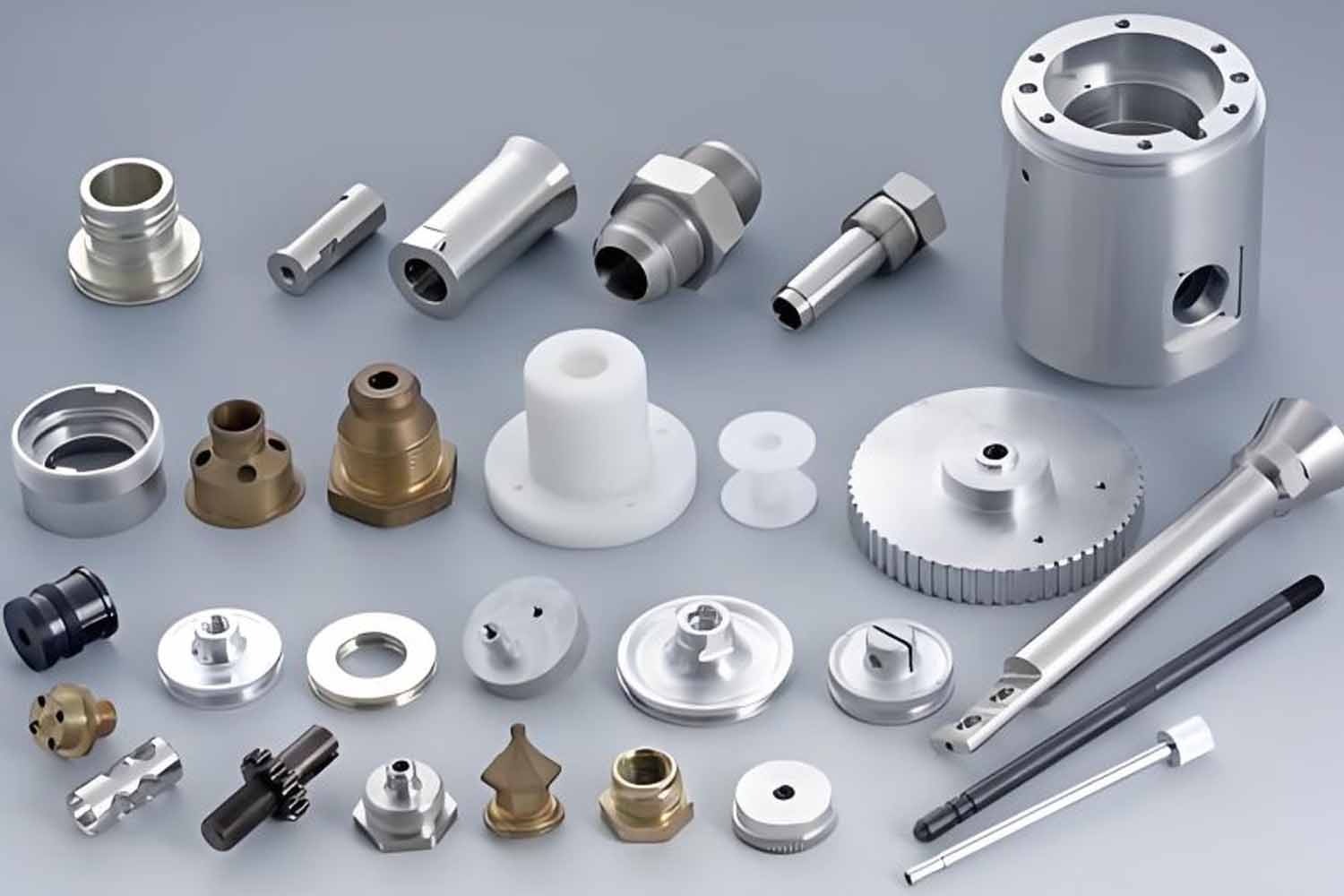
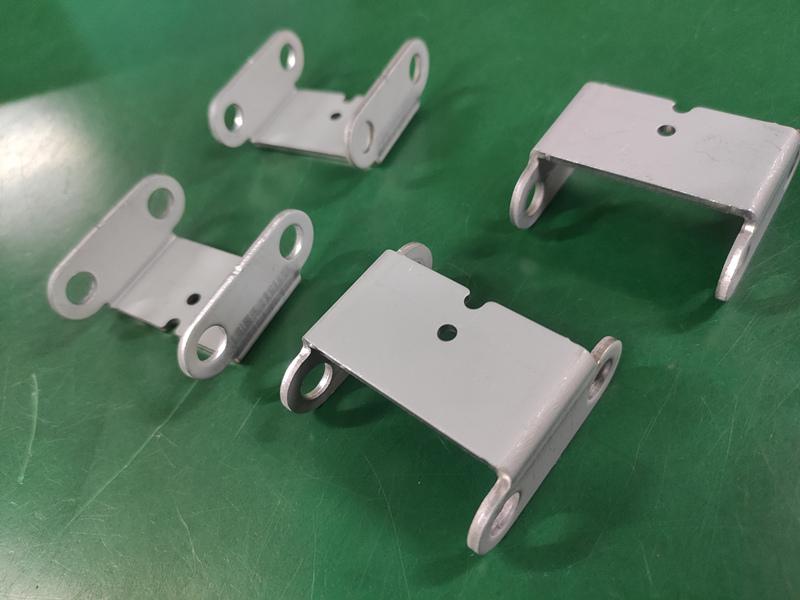
I’ve spent enough time around manufacturing floors to know one thing — nothing flies in aerospace without precision.
One wrong cut, and a component that looks perfect could fail in the air.
That’s where CNC machining steps in, and honestly, I’ve seen it save the day more times than I can count.
The aerospace industry depends on parts that fit within incredibly tight tolerances.
CNC machining makes that possible, whether it’s for an engine mount, landing gear part, or a custom bracket.
So, what is CNC machining for aerospace parts?
It’s the process of using computer-controlled tools to produce parts with extreme accuracy, often within a tolerance of ±0.001 inches.
This is not just nice to have — aerospace standards require it.
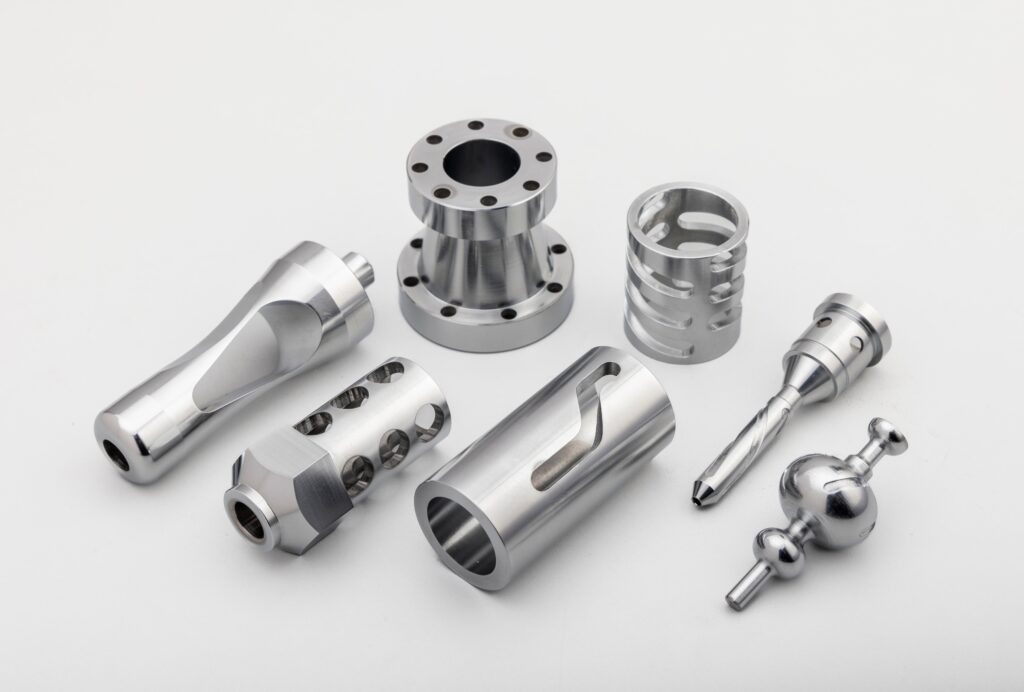
Types of Aerospace Parts Made with CNC Machining
In aerospace manufacturing, CNC machining plays a critical role in producing parts that meet precise design requirements. Every part, whether for an aircraft engine, fuselage, or avionics system, has a defined function and is made using specific CNC processes to achieve its required performance.
Below is a detailed breakdown of aerospace parts, their purpose, and the CNC processes used to manufacture them.
Engine Components
Turbine Blades
Turbine blades convert high-temperature, high-pressure gas into mechanical energy that drives the aircraft’s engine shaft. They must withstand extreme rotational speeds and heat.
CNC Process:
• Machined using 5-axis CNC milling to create the precise aerodynamic shape required for efficient airflow.
• EDM may be used to create intricate cooling channels within the blade.
• Surface polishing is applied to reduce drag and improve heat resistance.
Compressor Discs
Compressor discs hold the blades that compress incoming air before it enters the combustion chamber. They operate under high stress and must maintain perfect balance.
CNC Process:
• Produced using CNC turning for the outer profile and hub geometry.
• Milling is used to create attachment slots for the blades.
• Balancing and inspection are performed with a CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) to ensure symmetry.
Combustion Chamber Parts
The combustion chamber contains and controls the burning of fuel and air to generate thrust. Its walls must resist heat, pressure, and vibration.
CNC Process:
• 5-axis CNC milling to machine complex inner contours and ports.
• Precision drilling for fuel injector holes and cooling passages.
• Multi-axis machining allows for the seamless integration of mounting features.
Structural Parts
Wing Ribs and Spars
Wing ribs provide shape and structural support, while spars are the main load-bearing beams of the wing. Together, they handle aerodynamic forces during flight.
CNC Process:
• Machined from aluminium alloy billets or sheets using CNC milling to maintain consistent thickness and profile.
• Pocket milling removes excess material to reduce weight while preserving strength.
• Deburring ensures smooth edges to prevent fatigue cracks.
Landing Gear Brackets
Landing gear brackets secure the landing gear assembly to the aircraft structure, handling the stress of takeoff, landing, and taxiing.
CNC Process:
• Produced with CNC milling for mounting faces and bolt holes.
• CNC boring ensures a precise fit for attachment pins and bearings.
• Multi-axis machining allows the creation of complex bracket shapes from a single block of material.
Fuselage Frames
Fuselage frames form the skeleton of the aircraft’s main body, supporting the skin panels and distributing load forces evenly.
CNC Process:
• Large-format CNC milling machines carve out the frame’s profile from aluminium or titanium plates.
• Drilling and tapping for fasteners and joining points.
• Coordinate-based machining ensures all frames align perfectly for assembly.
Avionics Housings
Sensor Housings
Protect sensitive flight sensors from environmental hazards such as vibration, moisture, and electromagnetic interference.
CNC Process:
• CNC milling from solid aluminium or magnesium billets for maximum strength-to-weight ratio.
• Precision boring for mounting holes and internal compartments.
• Surface finishing to improve corrosion resistance and sealing surfaces.
Electronic Control Unit Enclosures
Enclosures house and shield the aircraft’s electronic control systems, ensuring safe and uninterrupted operation.
CNC Process:
• Multi-axis CNC milling creates complex internal compartments for circuit boards and connectors.
• CNC drilling for cable entry points and fastening holes.
• Electromagnetic shielding features are integrated during machining for better interference protection.
Fuel & Hydraulic System Parts
Fuel Pump Housings
Encase the fuel pump assembly, ensuring leak-free operation under pressure while protecting it from vibration and external damage.
CNC Process:
• CNC turning shapes the cylindrical body with precise wall thickness.
• Milling adds mounting flanges and connector points.
• Internal pocket machining forms chambers for pump components.

Injector Nozzles
Deliver fuel energy into the combustion chamber in a fine mist for efficient burning. Nozzles must have extremely accurate hole sizes and spray patterns.
CNC Process:
• Micro-CNC machining for ultra-small precision holes.
• EDM to create perfectly smooth fuel channels without deformation.
• Laser machining may be combined for ultra-fine outlet shaping.
Valve Bodies
Control the direction and flow of fuel or hydraulic fluid within the aircraft’s systems.
CNC Process:
• CNC milling and drilling create fluid channels with exact tolerances.
• Thread milling produces strong and accurate threaded ports for fittings.
• Surface finishing prevents corrosion and ensures smooth fluid flow.
Materials Used in CNC Machining Aerospace Parts
The choice of material in aerospace CNC machining is critical. Each material is selected based on strength, weight, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance.
Aluminum Alloys (7075, 6061, 2024)
Lightweight and strong, aluminum alloys are ideal for aircraft frames, wing parts, and housings. They are easy to machine and resist corrosion.
Titanium Alloys (Ti-6Al-4V)
Titanium is both strong and light, making it perfect for engine parts, landing gear, and high-stress structures. It also resists heat and corrosion.
Stainless Steels (17-4PH, 15-5PH)
Used for components that need high strength and wear resistance, such as brackets and shafts. These steels handle high loads without deforming.
Nickel Alloys (Inconel 718, 625)
Withstand extreme heat and pressure, making them suitable for turbine blades, exhaust parts, and engine casings.
Magnesium Alloys
Even lighter than aluminum, magnesium is used for non-structural parts where weight reduction is key.
Composite Materials (CFRP, GFRP)
Carbon and glass fiber composites are extremely strong yet light, perfect for fuselage panels and fairings.
Quality Standards and Certifications in Aerospace CNC Machining
In aerospace, quality is non-negotiable. Manufacturers follow strict standards to ensure every part meets safety and performance needs.
• AS9100 Certification – The main aerospace quality standard, covering manufacturing processes from start to finish.
• ISO 9001 – Ensures consistent quality management systems are in place.
• ITAR Compliance – Required for parts used in U.S. defense and space applications, controlling how technical data is handled.
• NADCAP – Oversees special processes like heat treatment, coatings, and welding.
• First Article Inspection (FAI) – Confirms the first produced part meets all design specifications before mass production begins.
• GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing) – Ensures parts meet exact dimensions and fits.
• CMM Inspection – Uses a coordinate measuring device to verify precision within microns.
• These certifications and inspections keep aerospace CNC parts reliable, safe, and compliant with global industry standards.
Aerospace CNC Parts Overview
|
Aerospace Part
|
How It’s Made
|
Material(s)
|
Benefit
|
|
Turbine Blades
|
5-axis milling, polishing
|
Titanium, Inconel
|
Heat resistance, engine efficiency
|
|
Wing Ribs
|
CNC milling from sheets
|
Aluminum 7075, 2024
|
Light, strong, fuel savings
|
|
Landing Gear Brackets
|
CNC turning, boring
|
Stainless steel, titanium
|
High load capacity
|
|
Avionics Housings
|
CNC milling, drilling
|
Aluminum, magnesium
|
Protect electronics, light weight
|
|
Fuel Pump Housings
|
CNC turning, milling
|
Stainless steel, titanium
|
Leak-proof, corrosion resistance
|
|
Satellite Housings
|
5-axis milling
|
Aluminum, CFRP
|
Light, stiff, space-grade
|
Product Examples from Yangsen
Custom Aerospace Brackets and Mounts
Brackets keep wires, tubes, and small devices secure inside aircraft. To make these, manufacturers use Yangsen Vertical CNC Machining Centers or compact 5-axis CNC machines.
Vertical CNC machines handle flat surfaces, drilling, and tapped holes with accuracy. 5-axis CNC machines allow angled cuts and undercuts in one setup, reducing time and improving precision. Yangsen’s CNC solutions keep hole locations exact and surface finishes smooth.
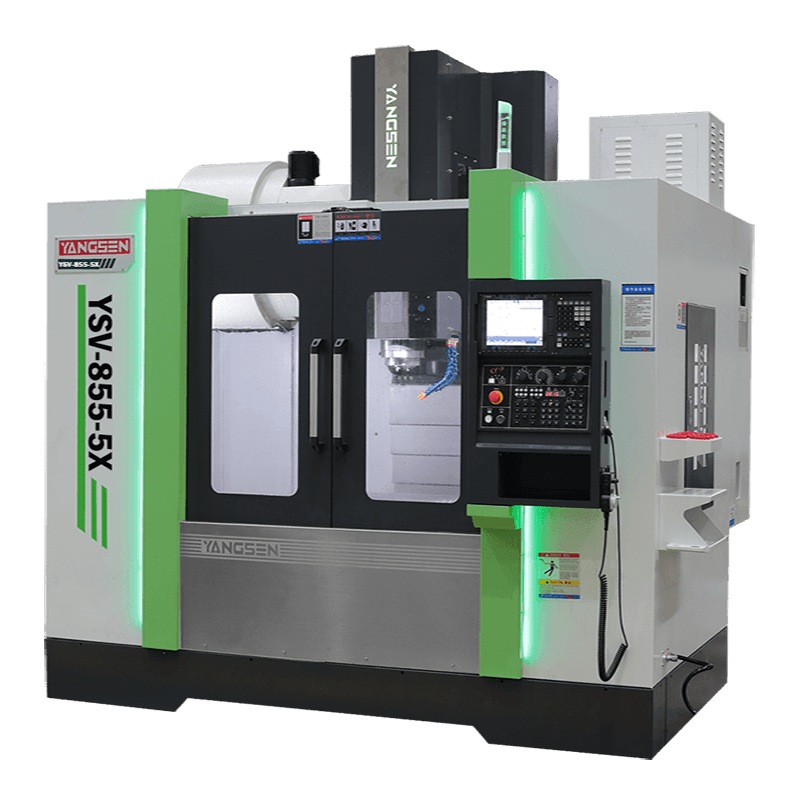

Turbine Blade Machining
Turbine blades require smooth, curved airfoils and exact dimensions. Shops rely on Yangsen 5-axis CNC milling machines to shape the blade profile and root in one run.
These multi-axis CNC machines remove the need for multiple setups, ensuring higher precision and better surface quality. Yangsen’s 5-axis models provide the fine control needed for engine-grade components.
Satellite Component Housings
Satellite housings must be lightweight but strong. Small housings are made using compact Yangsen 5-axis CNC machining centers, perfect for pockets, mounting faces, and cable channels.
Larger housings or panels use Yangsen gantry-style CNC machines, which offer large travel and stable support for oversized aerospace workpieces. These CNC machines allow milling, drilling, and fine finishing on one platform.
Aircraft Landing Gear Components
Landing gear components need heavy, rigid machining. Yangsen Horizontal CNC Boring Machines and Horizontal Machining Centers (HMCs) provide the strength to bore large holes and cut flat faces.
For shafts and axles, Yangsen CNC lathes are used for precision turning and final finishing. These CNC machines are built to hold the tight tolerances and surface finishes required for safe landing gear operation.
Benefits of Choosing CNC Machining for Aerospace Parts
CNC machining is the favored method for making aerospace parts because it delivers accuracy, speed, and reliability.
• High precision and tight tolerances – Aerospace parts must fit perfectly and perform under extreme conditions. CNC machines can work within microns, ensuring every dimension matches the design exactly.
• Ability to produce complex geometries – Aircraft and spacecraft designs often require curved shapes, deep pockets, and fine details. Multi-axis CNC machining allows these shapes to be made in one setup, reducing errors.
• Faster turnaround times – CNC programs can be adjusted quickly for prototypes or production runs. This means parts can be made faster without sacrificing quality.
• Consistent quality across large orders – Once a CNC program is set, the machine produces the same part every time, which is important for mass production.
• Stronger and lighter components – CNC machining allows precise removal of material to reduce weight while keeping structural strength, which is essential for flight performance.
• For aerospace manufacturers, these benefits make CNC machining the most reliable way to produce safe, high-performance parts at any scale.
Why Work with Yangsen for Aerospace CNC Machining
Yangsen has been supplying CNC machining of aerospace parts to both aircraft and space industries for years. Our team understands the strict standards, materials, and processes needed to make safe and reliable components.
Years of experience in aerospace manufacturing
We have worked on projects ranging from small aircraft brackets to high-performance turbine blades, giving us a wide base of knowledge.
Advanced CNC machines
Our shop uses multi-axis CNC machining centers and precision turning equipment from leading brands like Haas, DMG Mori, and Mazak. These machines allow us to work with tight tolerances and complex shapes.
Skilled engineers and machinists
Our team has the training and hands-on skills to turn designs into finished aerospace parts. They check every step to meet aerospace standards.
Global shipping and reliable timelines
Whether you need parts locally or overseas, we have reliable logistics partners to ensure your order arrives on time.
Proven project success
From satellite component housings to landing gear parts, we have completed projects that passed strict client and regulatory inspections.
With Yangsen, you get a supplier that combines precision technology, skilled people, and dependable delivery for aerospace manufacturing.

Conclusion
CNC machining plays an essential role in the aerospace industry. From engine components to structural parts, the process delivers the precision, potency, and reliability needed for flight and space applications. Every part must perform flawlessly under extreme conditions, and CNC technology makes that possible with unmatched accuracy.
Yangsen has the expertise, advanced machines, and skilled team to meet the strict demands of aerospace manufacturing. We work with top-grade materials, follow industry certifications, and produce parts that pass the toughest inspections.
Contact us today for your aerospace part needs and let Yangsen deliver the quality and precision your project demands.






























